Are you wondering if you need to take vitamins? Maybe you have the question, why do I need to take vitamins, since you get them from food already? In this video, we look at some of the things that come to mind with this question like why people are deficient to begin with, the testing and symptoms that help inform us if you are deficient. In addition we look at what to do when you are deficient and how to get your levels back up if you are not getting enough through the food. Does this mean you just need to take more orally or get injections?
So if you want to understand if you need to take vitamins and what to do when you level are low, keep reading.
Do I Need To Take Vitamins and RDA?
This question is important because there is a lot of information on the internet and otherwise about the need to take vitamins but not all of it is accurate, some of it is misleading, and some of it's actually dangerous. With that being said, the main thing that I hope you get out of this article is the important role vitamins play in our health. More specifically, I hope you'll gain a better understanding of why you might need a vitamin and or mineral supplement. We also address questions like, who is a candidate for vitamin supplements? How do we know when you are, or not a candidate? Where do vitamins minerals nutrients etc work in the body? What is the best delivery form for these vitamins nutrients minerals? A lot of these questions and topics can be expanded on so think about this as a foundation. If you do have questions about some of the specifics of what is covered, just drop it in the comment section.
The first thing to discuss with the topic, do I need to take vitamins, is the RDA. RDA stands for the recommended daily allowance and that comes from the FDA. It represents the minimum amount needed to prevent serious medical issues from lack of a specific vitamin. There are specific conditions associated with a lack of each vitamin that we know about. There is Scurvy for vitamin C,Beriberi for thiamin or B1 deficiency and many other well documented health issues from vitamin deficiency. The issue with the RDA is that it does not account for many different variables of individual human physiology and it's basically looking to prevent serious illness from vitamin deficiency. As a result, the RDA is not the recommended range for optimal health. Instead it is the amount needed to prevent serious disease in the population as a whole. That being said, there are a lot of reasons why you might need much more than what the RDA suggests. This is where individual medicine comes in. So let me give you some examples.
Conditionally essential refers to the body's need for higher amounts of certain vitamins and nutrients during periods of stress on the body. These are periods where there are certain physiological processes happening in the body and stressing certain systems out. As a result, you may need more of a certain nutrients vitamins etc.
One example of this that comes to mind is with vitamin C. Our bodies cannot make vitamin C but we do get it from food. During periods of infection, for instance, we may need more vitamin C. Vitamin C has been shown to increase immune activity and shorten the duration of sickness. During periods of high amounts of immune activity our bodies are burning through vitamin C at a more rapid rate. That condition requires more vitamin C for that period of time. If you are taking the minimum amount needed, you can prevent scurvy. If you take more than the minimum amount needed you can get rid of your cold a lot quicker. There are many other examples like this.
So the RDA is concerned with preventing serious illness from lack of a vitamin or mineral. This gives us a benchmark or starting that you really don't want to go below. However, this is not really the upper limit either. It is a bit misleading to say that the RDA is what everyone needs because some people need a lot more. So do you know if you're meeting the RDA for your nutrition intake with just food alone? Let me know in the comment section below.
Do I Need To Take Vitamins? I eat healthy.
The CDC reported in 2009 that only about thirty percent of people get three or more servings of fruits or vegetables per day. We all know that this is where most of our vitamins and nutrients are coming from. Of course, some come from animal protein and different organ meats and things like that. Most of us are getting the majority of our vitamins and nutrients from plant sources. After all, the plant sources are what the animals eat too. Plants are very important part of our nutrition. If you are only eating three or four servings of fruits and vegetables (or possibly less), you may be very micronutrient depleted (vitamins minerals etc).
The other thing to think about is what has occurred with our soil and the agricultural industry over the last 100 years. What does this do to the nutrient content in the plants that we are actually eating on a day-to-day basis. The nutrients in the plants come from the soil. If the soil is depleted, those plants are going to be depleted in specific nutrients as well. This is because a lot of these newer farming practices are more concerned with quantity not quality. As a result they are not rotating crops properly. Using the same crop over and over will continue to pull those nutrients out leaving depleted soil. Ideally crops should be rotated to give the soil a chance to naturally replenish any nutrients that were depleted. There are certain plants and crops that should be used to do this. Over the last hundred or so years this practice has lost favor especially with big agricultural farming. As a result, we have soil and food that is really depleted and devoid of a lot of the vitamins and minerals that we need to meet the minimum amount not to mention optimal amounts.
With that being said, how many fruits and vegetables do you think you need to meet the RDA for all your vitamins and minerals? Let me know what you think in the comment section. Some of us consume things on a daily basis that may be depleting our nutrient status or causing us to get rid of certain vitamins and minerals faster than we should. Alcohol and caffeine are common examples that deplete your vitamin levels nutrient levels etc.
So if you are following along, you might say, "I already eat a good quantity of fruits and vegetables, I don't drink caffeine or alcohol, so do i need to take vitamins?" This leads us into the next thing we should look at with this question and that is absorption.
Do I Need To Take Vitamins, What about Absorption?
Depending on what you eat, you may be consuming plenty of vitamins, minerals, and nutrients. However, there can still be a problem with that getting into your body, meaning you may not be absorbing those nutrients. Let's look at some digestive issues and conditions that suggest you may not be absorbing or have compromised absorption. There are actual digestive system issues that do this like pernicious anemia, Gastroesophageal reflux, IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome), IBD like Crohn's, and ulcerative colitis. There are also functional digestive issues (leading to inflammation or altered bowels) that can do this too. These are usually things that you see a GI doctor for and don't find anything (and say everything looks normal). Still you are having symptoms and so it would be considered IBS or functional digestive disorder. Symptoms might be loose stools, indigestion, gas, bloating, acid reflux, constipation etc.
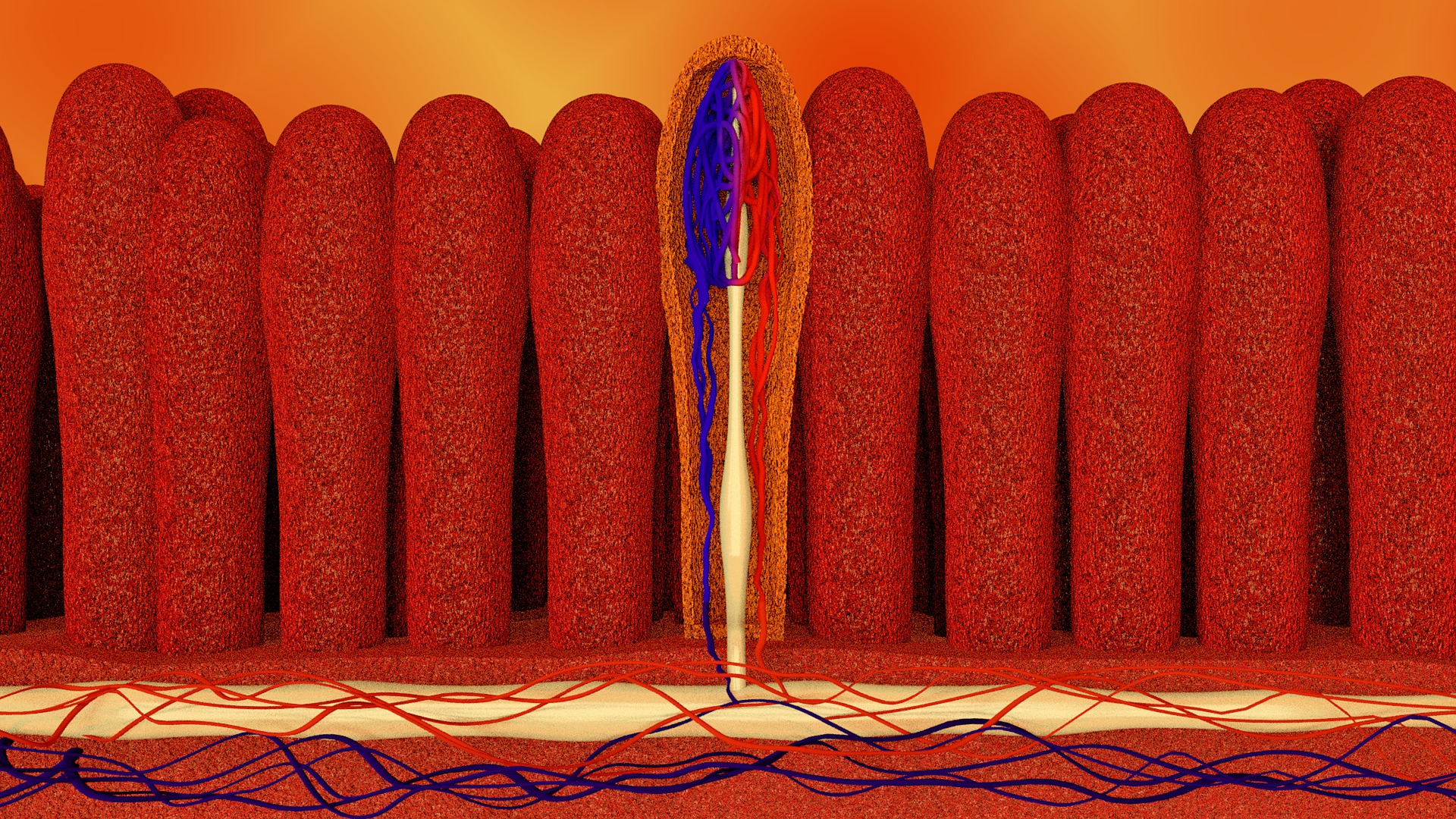
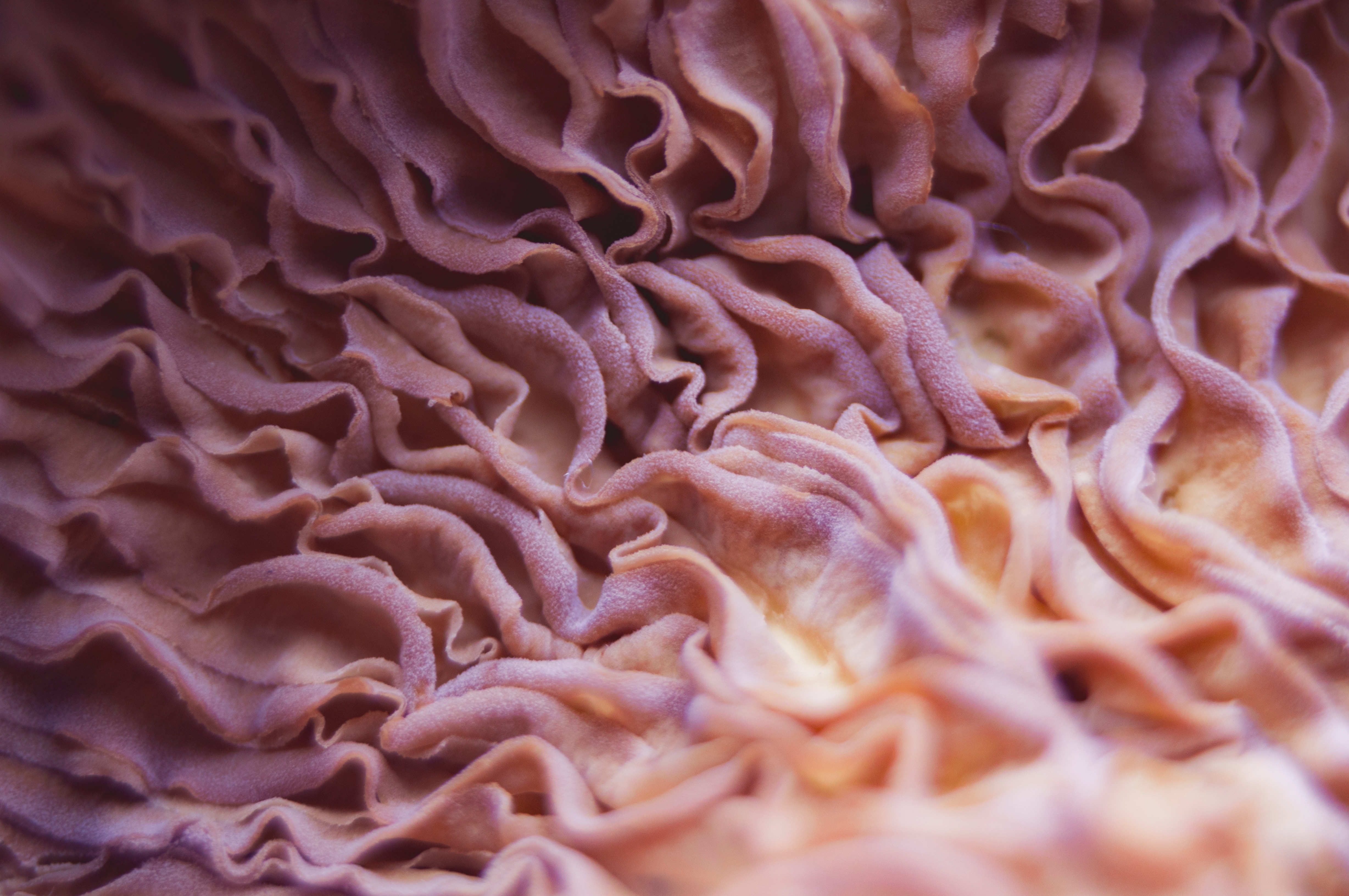
This picture above is of the villi and microvilli of the digestive tract. The open section is a cross section of the intestinal lining cell. All the little projections are where the food is absorbed through. These can get damaged from inflammation and which means you're not getting as much nutrients. As food is being broken down it passes through these digestive cells and into your body. If you are not absorbing these foods, you are obviously not doing yourself any good by eating more fruits and vegetables. It is better than eating a poor diet but you still need to take care of the absorption issue. It might mean that you need more of specific vitamin, nutrient, minerals etc depending on what's going on.
Pernicious anemia, for instance, is an autoimmune condition where your body attacks the intrinsic factor that is needed to absorb vitamin B12. If you have this, all your vitamin B12 in the world is not going to help you. You actually need to take injections or take a sublingual B12. All this absorption stuff is also important so if you have a lot of inflammation going on it's important to look at that and address it. It also points to the fact that you may need to take more vitamins
Now you might say, "I consume a good quality diet (lots of fruits and vegetables), I don't consume any caffeine or alcohol, and I don't have any apparent digestive issues, do I need to take vitamins?" Well let's look at another issues that may require you to take more vitamins.
Do I Need To Take Vitamins, What about Medications?
Some medications definitely increase the need to take vitamins. It's because they increase the excretion of vitamins, decrease the absorption of vitamins, or increase the demand for certain vitamins in the body. Let's look at a few examples of that. Antidepressants like tricyclic antidepressants are a family of medications one is called Elavil. They are going to increase the need for B vitamins and they can also actually deplete your B vitamin levels. Diabetic medications like metformin deplete B12, probably folate, and magnesium. If you are taking metformin, you may need more of these specific vitamins. At least it means you should be evaluated a little bit more thoroughly for vitamin deficiencies.

Acid reducing medications are a big one because they deplete the stomach acid and the ability to produce intrinsic factor. Intrinsic factor was mentioned earlier. As a result of decline in intrinsic factor they decrease B12 absorption. Also on the absorption side you will have less magnesium, zinc, calcium, folate, iron etc. All of these vitamins can be depleted just by taking certain acid-reducing medications. This occurs over time and will not happen just from taking it once or for short periods of time It is the long insidious consumption of these medications that will deplete your vitamin stores. If you're taking medications, it's important to look at what they might deplete in your body.
Alright so now you say, "I consume plenty of fruits and vegetables, I don't consume any caffeine or alcohol, I don't have any apparent digestive symptoms and I don't take any medications, do I need to take vitamins?"
What about Genetics?
Do my genetics cause my body to need more of certain vitamins minerals etc? When we refer to genetics, in this case, we are referring to single nucleotide polymorphisms or SNP's. This is a single point along your genetic code that is changed. The gene is the code or the blueprint that then tells your body how to make the protein. When there is a change in the the gene, the outcome of the protein changes. In cases of significant single point mutation or significant SNP's, the outcome of that protein will be more significant. This may increase the demand for certain nutrients or certain vitamins that the body needs.

You can think about it as an analogy to a car factory. If we have a car factory, the blueprint for the car is what's being altered. When altered the car may come out with three wheels instead of four. As you might guess that car will still be somewhat functional with three wheels. You might be able to get it to roll with some balancing efforts but it's not going to roll very well. It will not be as functional as if there are four wheels. This same thing happens with the body when there is a significant SNP.
Vitamins and nutrients act as cofactors, which we will discuss more below. They help support that fourth wheel so that things still work. The cofactors will not make it work as good as new though. Why do we care about this? We can support the enzymes with nutrition when those enzymes or proteins are altered due to genetics. This field of medicine is called nutrigenomics. It is the use of nutrition to improve your health based on specific genetic alterations.
An example that many people maybe have heard of is the MTHFR enzyme. Everyone has an MTHFR enzyme functioning in their body. MTHFR stands for methyltetrahydrofolate reductase. This enzyme turns different forms of less active folate into more active folate. When you have an alteration in the MTHFR enzyme, due to one of these single nucleotide polymorphisms, it can reduce the functionality. A lot of people do have this MTHFR alteration, as much as seventy percent of the population. However not all of the alterations are as significant as the other ones. Somewhere closer to a third of the population have moderate to severe MTHFR genetic alterations. One of the most common symptoms that people will have is fatigue depression and mental fog. Those with significant MTHFR are also more prone to blood clots related to homocysteine.
There's also one SNP known as COMT. COMT stands for catechol methyl transferase and this enzyme facilitates the breakdown of stimulating neurotransmitters known as catecholamines. These are things like adrenaline, dopamine etc. When you have this alteration, these build up in your system making you feel a little bit more stimulated and anxious. You may also have more insomnia and high blood pressure issues and even bipolar. These are all associated with the COMT SNP. There are many other examples of the single nucleotide polymorphisms where a vitamin or mineral is needed in higher amounts in order to allow that enzyme to function properly. There are also some problems that can happen from vitamin mineral transporters. These transport things like thiamine, magnesium and other nutrients. So the nutrients can get into the body but they just can't be transported into the cells and tissues well.
These are some of the things you can look at through doing a genetic analysis and looking deeper at your genetics. The bottom line is genetics do play a role in our need for more vitamins. For some people it is very important and others not so much.
So now back to our question, if I consume enough, don't have any caffeine or alcohol, have good absorption, don't take any medications, and no genetic issues do I need to take vitamins? If this is the case for you, chances are you don't have a vitamin deficiency. Still another way to get at this question is do you have any signs and symptoms that may suggest you have a vitamin deficiency.
Testing to Determine, If I Need To Take Vitamins
Of course, you might be asking, why can't i just check to see if i have a vitamin deficiency? Yes you can test for vitamins but you may not catch all of the issues that are occurring. In the case of transport issues you may be sub-optimal in certain vitamins. Yet when you do a blood test it can look normal. Functionally speaking you may have symptoms indicating there is something wrong but the blood test wouldn't show it. The vitamin level looks fine but your tissues are actually asking for more because they are not delivered to the tissues. That's why signs and symptoms are helpful as they can suggest when you need more of a specific vitamin.
Signs are objective measurements like lab tests and things that we can see and measure. Symptoms are more subjective things you're feeling personally and can't necessarily be measured. First let's look at some of these signs. A few signs that are helpful are macrocytosis, homocysteine, and certain vitamin levels. Macrocytosis can be observed on standard blood tests during a physical exam.
A CBC known as complete blood count looks at red blood cells and white blood cells. In the red blood cell part you can look at the relative size of those red blood cells. When the cells start to enlarge that's called macrocytosis. That is an indicator of B12 and folate deficiency. What's happening there is the cells start out small then they get bigger and bigger. Right before they're ready to divide they are in a larger state and then they divide. They split in the middle and divide. Part of that splitting requires DNA replicating. Half of that DNA goes to one cell and the other half goes to the other. The DNA is really dependent on B12 and folate. When you don't have enough of those you'll have more cells stuck in the larger state. That's called macrocytosis. Each lab has a slightly different reference range but the higher the number the more likely thee is a problem. That test is on the CBC that looks at this is called MCV.
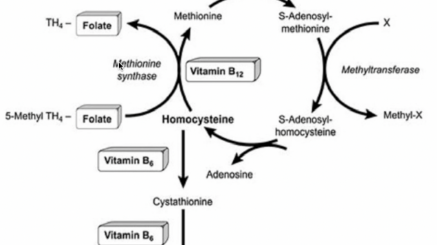
Another test is called homocysteine. This can also be elevated when there is B12 and folate deficiency as well. Homocysteine elevation can also be an indicator of B12 deficiency. Some of these vitamins can be measured directly in your blood. You can measure B12, riboflavin and other vitamin levels. A lot of times they're not covered by insurance and in some cases they are not very accurate. So it's not always telling us when you need more of these vitamins and that's where functional assessment, intracellular vitamin, etc come into play.
There are tests like red blood cell folate and other red blood cell tests that can be more useful in identifying when there's a intracellular need versus just what's floating around in the blood. Not all vitamins can be checked that way though. So depending on which vitamin you're looking at, you may have to do it through the serum. Another functional way to look at vitamin status is called a white blood cell nutrient analysis. This test is a functional way to look at whether or not your cells have enough of these vitamins and nutrients. This test takes your white blood cells and it puts them on petri dish. Each petri dish is depleted in one specific vitamin mineral or nutrient. The test then looks at the length of time the white blood cells live in the depleted petri dish compared to controls. This tell us what the functional stores are of that vitamin or nutrient. When they are devoid of those nutrients, they don't live long. Cell should be able to sustain themselves for a period of time without getting nutrients from the environment. The length of time your cells live compared to the reference range can be an indicator of deficiency. This specialty lab test is done by Spectra Cell.
Another functional tests similar to this is called an organic acid test. This test will not measure every single nutrient or vitamin that have a questions about. It can cover a lot of them though. This test will looks for metabolites that are elevated when there is a deficiency of a vitamin, nutrient, or mineral and urine levels of actual vitamins.
Now you should have a very good understanding of how to look at the question, "do I need to take vitamins." If you have questions about the content in this article, please ask it in the comment section below.
If you want a customized plan on which vitamins you need to take, click in the link below to get started.












 It's possible that the increased DHT levels in the creatine group was due to an anomaly with one or two people in that group, or vice versa with the placebo group. For instance, maybe something was going on with the placebo group that caused their DHT levels to be higher at the start of the study, such as getting better sleep. Also, while the study was being conducted, the control group had a slight decrease in their DHT levels.
It's possible that the increased DHT levels in the creatine group was due to an anomaly with one or two people in that group, or vice versa with the placebo group. For instance, maybe something was going on with the placebo group that caused their DHT levels to be higher at the start of the study, such as getting better sleep. Also, while the study was being conducted, the control group had a slight decrease in their DHT levels..jpg?width=6000&height=3376&name=robina-weermeijer--szKjHyPq28-unsplash%20(1).jpg)
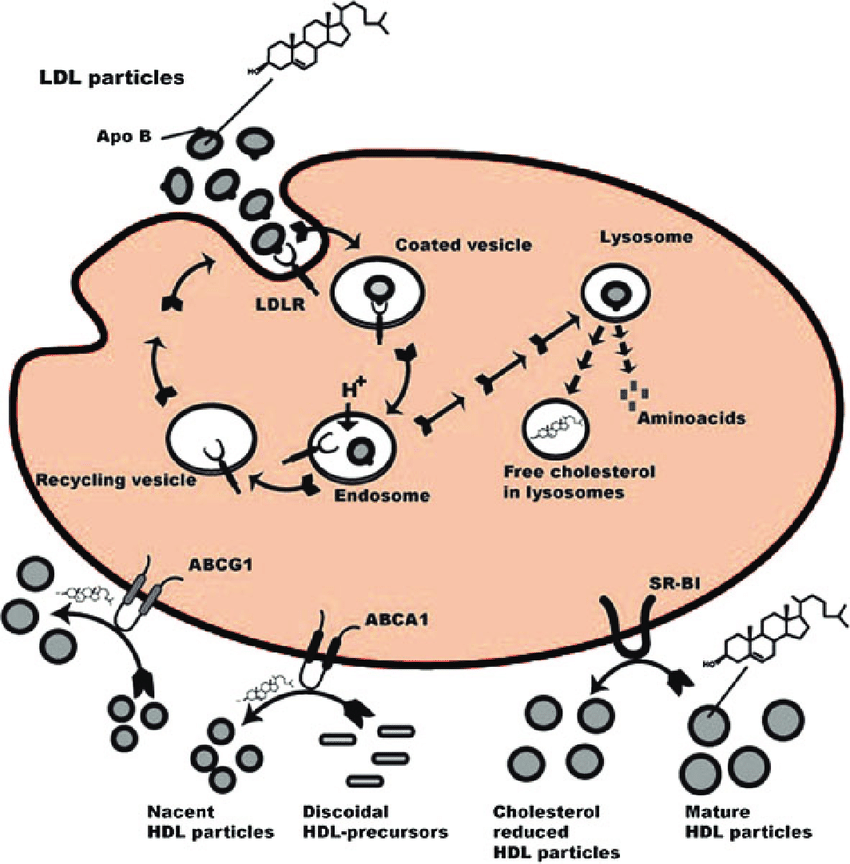
 Total serum cholesterol, triglycerides, and other cholesterol markers are
Total serum cholesterol, triglycerides, and other cholesterol markers are




 To rule out any impact of exercise, they also measured creatinine kinase. The also controlled for the
To rule out any impact of exercise, they also measured creatinine kinase. The also controlled for the 






 In practice, when people take vitamin D it commonly improves their energy levels and provides additional support to their immune system. If you are someone that gets sick a lot you may be vitamin D deficient. The more of these things that align, the more likely you are to be vitamin D deficient. In this case it makes getting your levels checked more important.
In practice, when people take vitamin D it commonly improves their energy levels and provides additional support to their immune system. If you are someone that gets sick a lot you may be vitamin D deficient. The more of these things that align, the more likely you are to be vitamin D deficient. In this case it makes getting your levels checked more important. 











 If you are taking a lot of Tylenol for pain, for instance, you may need to find a different pain alternative. You should talk to your doctor about different options for that. If you consume a lot of alcohol or even mild to moderate amounts, you may need to cut that out or cut back to see if that has an effect on your liver enzymes. When you are consuming a lot of alcohol, you may need extra help through a medical detox, for instance. In the case of fatty liver, or what's also known as NASH or non-alcoholic steato-hepatitis, the problem occurs from excess triglycerides. Excess triglycerides usually occur from excess carbohydrate intake. It would make sense that lowering your carbohydrate intake, specifically things like the refined carbohydrates would improve fatty liver. Sometimes there is combination or multiple things causing your liver inflammation. To find out, get some lab work done or diagnostic tests to get a clear understanding of the cause. From there you will have a better idea how to lower the numbers.
If you are taking a lot of Tylenol for pain, for instance, you may need to find a different pain alternative. You should talk to your doctor about different options for that. If you consume a lot of alcohol or even mild to moderate amounts, you may need to cut that out or cut back to see if that has an effect on your liver enzymes. When you are consuming a lot of alcohol, you may need extra help through a medical detox, for instance. In the case of fatty liver, or what's also known as NASH or non-alcoholic steato-hepatitis, the problem occurs from excess triglycerides. Excess triglycerides usually occur from excess carbohydrate intake. It would make sense that lowering your carbohydrate intake, specifically things like the refined carbohydrates would improve fatty liver. Sometimes there is combination or multiple things causing your liver inflammation. To find out, get some lab work done or diagnostic tests to get a clear understanding of the cause. From there you will have a better idea how to lower the numbers. 
 These enzymes carry out some of the most fundamental aspects of what your liver does, detoxify. When they are high it does mean that you have hepatitis. Now hepatitis is really just inflammation of the liver. If you break down the words into it's root, this is clear. 'Hepa' means liver and 'itis' means inflammation, therefore inflammation of the liver. Anytime the liver enzymes are high, that means that you have hepatitis. A lot of times when people hear hepatitis, they automatically think they have some kind of virus. This is not necessarily true.
These enzymes carry out some of the most fundamental aspects of what your liver does, detoxify. When they are high it does mean that you have hepatitis. Now hepatitis is really just inflammation of the liver. If you break down the words into it's root, this is clear. 'Hepa' means liver and 'itis' means inflammation, therefore inflammation of the liver. Anytime the liver enzymes are high, that means that you have hepatitis. A lot of times when people hear hepatitis, they automatically think they have some kind of virus. This is not necessarily true. 

.jpg?width=1920&name=disease-4392168_1920%20(1).jpg)













 you donate blood, you become anemic, or just iron deficient. The measurement they use for donation eligibility is hemoglobin. You can have enough hemoglobin and be low to low normal on your stored iron (ferritin). So you may not low enough to be ineligible but on the edge. Then you donate which drops you into low. If you're not consuming enough iron in your diet or had a diet change it may take a while for your iron levels to normalize. This problem does not come up commonly but most iron deficiency does not present in males either.
you donate blood, you become anemic, or just iron deficient. The measurement they use for donation eligibility is hemoglobin. You can have enough hemoglobin and be low to low normal on your stored iron (ferritin). So you may not low enough to be ineligible but on the edge. Then you donate which drops you into low. If you're not consuming enough iron in your diet or had a diet change it may take a while for your iron levels to normalize. This problem does not come up commonly but most iron deficiency does not present in males either. 

 Now contrast this with progesterone. Progesterone acts to antagonize or block the effects of aldosterone and other mineral corticoid hormones from binding to the kidneys. This leads to less sodium retention and a corresponding decrease in water retention. Only "bioidentical" progesterone has that effect. However not all forms of progesterone have that effect. For instance, other synthetic type of progesterones known as progestins do not. Progestins don't have the counter balance effect on sodium retention and mineral corticoids. So for females on hormone replacement therapy or birth control, this could be the reason you have so much fluid retention. Birth control pills contain progestins and not progesterone. For females that are postmenopausal they may not be taking any progesterone or they may be taking progestins. In some cases, women just take estrogen in the form of estradiol. This can lead to a relative increase in sodium retention leading to a puffy feeling and weight gain. This usually doesn't happen all at once. It happens over a long-term, maybe after you're on it for several months or more.
Now contrast this with progesterone. Progesterone acts to antagonize or block the effects of aldosterone and other mineral corticoid hormones from binding to the kidneys. This leads to less sodium retention and a corresponding decrease in water retention. Only "bioidentical" progesterone has that effect. However not all forms of progesterone have that effect. For instance, other synthetic type of progesterones known as progestins do not. Progestins don't have the counter balance effect on sodium retention and mineral corticoids. So for females on hormone replacement therapy or birth control, this could be the reason you have so much fluid retention. Birth control pills contain progestins and not progesterone. For females that are postmenopausal they may not be taking any progesterone or they may be taking progestins. In some cases, women just take estrogen in the form of estradiol. This can lead to a relative increase in sodium retention leading to a puffy feeling and weight gain. This usually doesn't happen all at once. It happens over a long-term, maybe after you're on it for several months or more. 







 One of the things that can cause high iron levels is called hemochromatosis. Hemochromatosis is the disease state caused by high iron. It occurs due to a genetic abnormality if increased iron absorption through the digestive tract. When that happens your body tends to accumulate more iron. For females this problem tends to not show up early in life, if they are having normal menstrual cycles. It still can happen, but it is more common after they go through the menopause or stop mensuration. Women can still have the genetics of hemochromatosis but because they have menses their iron levels do not get high.
One of the things that can cause high iron levels is called hemochromatosis. Hemochromatosis is the disease state caused by high iron. It occurs due to a genetic abnormality if increased iron absorption through the digestive tract. When that happens your body tends to accumulate more iron. For females this problem tends to not show up early in life, if they are having normal menstrual cycles. It still can happen, but it is more common after they go through the menopause or stop mensuration. Women can still have the genetics of hemochromatosis but because they have menses their iron levels do not get high. 
 Putting yourself in caloric restriction and reduced protein (often vegan and vegetarian) diets will raise your sex hormone binding globulin. This may be more of an indirect route because of the effect on insulin. We know that insulin is a stimulus to lower your sex hormone binding globulin. Insulin goes up in response to things like eating a diet high in carbohydrates and protein. So if you are eating less of these, insulin goes down and SHBG goes up. There is also insulin like growth factor which is more of a growth hormone signal. Lower amounts of this will also raise sex hormone binding globulin. So if you are someone that is doing a lot of fasting or trying to lose weight and restricting calories, this may be why you have elevated sex hormone binding globulin.
Putting yourself in caloric restriction and reduced protein (often vegan and vegetarian) diets will raise your sex hormone binding globulin. This may be more of an indirect route because of the effect on insulin. We know that insulin is a stimulus to lower your sex hormone binding globulin. Insulin goes up in response to things like eating a diet high in carbohydrates and protein. So if you are eating less of these, insulin goes down and SHBG goes up. There is also insulin like growth factor which is more of a growth hormone signal. Lower amounts of this will also raise sex hormone binding globulin. So if you are someone that is doing a lot of fasting or trying to lose weight and restricting calories, this may be why you have elevated sex hormone binding globulin. 
 When you consume fats some are turned into ketones for fuel and most are stored in the body as fat. However, when you don't consume much carbohydrates or protein and you do consume lots of fats, less of the fat is stored and most is turned into ketones to be used as fuel.
When you consume fats some are turned into ketones for fuel and most are stored in the body as fat. However, when you don't consume much carbohydrates or protein and you do consume lots of fats, less of the fat is stored and most is turned into ketones to be used as fuel.  the shoot part as related to sympathetic activity. These refer to two parts of the nervous system that control our state of relaxation and excitement. The parasympathetic activity is related to rest and digest. This activity is associated with relaxation, calming and blood flow and dilation of the arteries. If you are not able to get or maintain an erection, this could be that you have too much anxiety, worry, and cortisol. Cortisol definitely can have a stress provoking activity. It puts you closer to that stress threshold. Another way to think about it is the time to irritability or anxiety is smaller. So there is a thinner layer between when you feel calm and when you feel agitation, anxiousness or worry.
the shoot part as related to sympathetic activity. These refer to two parts of the nervous system that control our state of relaxation and excitement. The parasympathetic activity is related to rest and digest. This activity is associated with relaxation, calming and blood flow and dilation of the arteries. If you are not able to get or maintain an erection, this could be that you have too much anxiety, worry, and cortisol. Cortisol definitely can have a stress provoking activity. It puts you closer to that stress threshold. Another way to think about it is the time to irritability or anxiety is smaller. So there is a thinner layer between when you feel calm and when you feel agitation, anxiousness or worry. 
 you take too much or don't get it quite right. If you are already significantly deficient and you start taking a moderate to higher doses of iodine it could cause problems. Specifically it can shift your body into thyrotoxicosis which is a severe hyperthyroid state. In this situation the person will have palpitations, anxiety, sweating, can't sleep, etc. It is a very uncomfortable state.
you take too much or don't get it quite right. If you are already significantly deficient and you start taking a moderate to higher doses of iodine it could cause problems. Specifically it can shift your body into thyrotoxicosis which is a severe hyperthyroid state. In this situation the person will have palpitations, anxiety, sweating, can't sleep, etc. It is a very uncomfortable state. 




![Figure 6.13, [Synthesis of histamine and serotonin...]. - Neuroscience - NCBI Bookshelf](https://www.swintegrativemedicine.com/hs-fs/hubfs/Figure%206.13,%20%5BSynthesis%20of%20histamine%20and%20serotonin...%5D.%20-%20Neuroscience%20-%20NCBI%20Bookshelf.jpg?width=1275&name=Figure%206.13,%20%5BSynthesis%20of%20histamine%20and%20serotonin...%5D.%20-%20Neuroscience%20-%20NCBI%20Bookshelf.jpg)
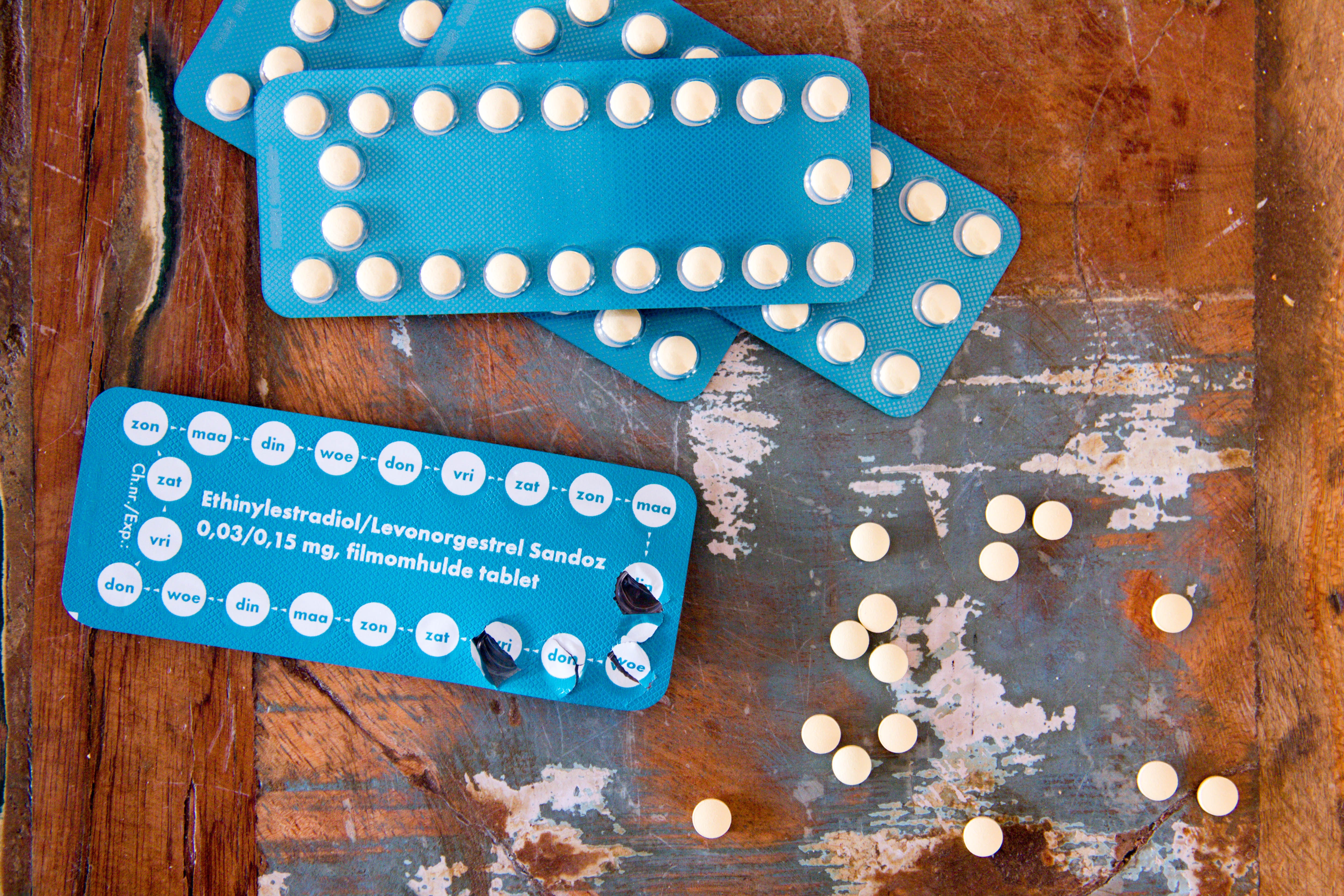





 The last scenario I wanted to discuss is with females taking birth control.
The last scenario I wanted to discuss is with females taking birth control. 




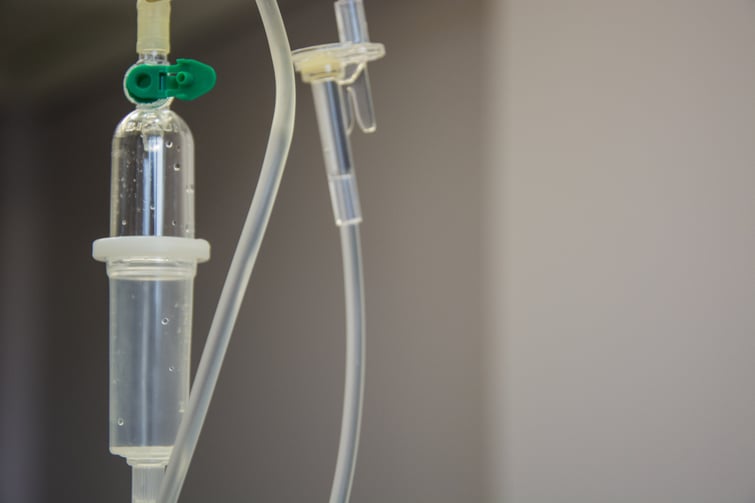





 Vitamin b12 in
Vitamin b12 in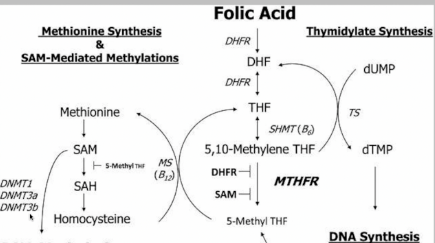





 Specifically the lower carb diet tends to create a greater reduction in total cholesterol and low density lipoprotein and create a greater increase in high density lipoprotein. All of these provide a superior reduction in cardiovascular risk (Hu et al., 2012).
Specifically the lower carb diet tends to create a greater reduction in total cholesterol and low density lipoprotein and create a greater increase in high density lipoprotein. All of these provide a superior reduction in cardiovascular risk (Hu et al., 2012).
 insufficient levels there is no reason to assume that you are doing yourself harm by taking them. If you don't have insufficient levels to being with, taking the enzymes will not provide any benefit and therefore you should not take them. If you are deficient however the benefit to taking them far outweighs and potential risk of down regulating your digestive enzyme production. Still I could not find documentation to support the claim that taking digestive enzymes will down regulate your bodies production of digestive enzymes.
insufficient levels there is no reason to assume that you are doing yourself harm by taking them. If you don't have insufficient levels to being with, taking the enzymes will not provide any benefit and therefore you should not take them. If you are deficient however the benefit to taking them far outweighs and potential risk of down regulating your digestive enzyme production. Still I could not find documentation to support the claim that taking digestive enzymes will down regulate your bodies production of digestive enzymes. 



 by many different researchers. Most of this research suggests that aerobic exercise (like jogging, hiking) is a superior form of exercise to loose weight when compared to weight lifting type exercise alone.1 This makes sense since you would tend to burn more calories this way. When most people start exercise they typically choose aerobic type exercise over weight lifting alone. While on this topic it is important to point out that the time you spend exercising is not as important as the work you do. So for instance, if you run 1 mile and it takes you 5 minutes or 20 minutes these would be considered somewhat equal in terms of their benefit. In fact, it may be more beneficial to do it in the shorter duration. If this means the exercise you do has a higher intensity. This link below has more information on this.
by many different researchers. Most of this research suggests that aerobic exercise (like jogging, hiking) is a superior form of exercise to loose weight when compared to weight lifting type exercise alone.1 This makes sense since you would tend to burn more calories this way. When most people start exercise they typically choose aerobic type exercise over weight lifting alone. While on this topic it is important to point out that the time you spend exercising is not as important as the work you do. So for instance, if you run 1 mile and it takes you 5 minutes or 20 minutes these would be considered somewhat equal in terms of their benefit. In fact, it may be more beneficial to do it in the shorter duration. If this means the exercise you do has a higher intensity. This link below has more information on this. 



.jpg?width=550&name=800px-Usnea_1_(2005_07_19).jpg)
 therapy the hormones are contained in a compact pellet-like solid structure. They are usually less than 1cm in size containing the desired hormone in the specified strength. They are inserted under the skin by a doctor using a minor surgical procedure that takes about 15 minutes to perform. Theincisions requires suture or butterfly for closure.
therapy the hormones are contained in a compact pellet-like solid structure. They are usually less than 1cm in size containing the desired hormone in the specified strength. They are inserted under the skin by a doctor using a minor surgical procedure that takes about 15 minutes to perform. Theincisions requires suture or butterfly for closure. production of this enzyme. Thus, any alteration in the structure of this gene (MTHFR gene mutation) will result in functional or absolute deficiency of MTHFR enzyme and inability to utilize folate.
production of this enzyme. Thus, any alteration in the structure of this gene (MTHFR gene mutation) will result in functional or absolute deficiency of MTHFR enzyme and inability to utilize folate. some T3) which are important in the regulation of the rate of various biochemical reactions in the body. These hormones influence, metabolism, body temperature, heart rate, and protein synthesis, for instance.
some T3) which are important in the regulation of the rate of various biochemical reactions in the body. These hormones influence, metabolism, body temperature, heart rate, and protein synthesis, for instance. the application of electric currents to such needles.
the application of electric currents to such needles. 
 fluctuations. With menopause the cessation of menses is also marked by a decline in hormone levels and sometimes mood too. Instead of emotional ups and downs there is often more of an emotional downturn. Not all women that go through menopause have this though. The menopausal period is often characterized by many unwanted symptoms such as hot flashes, sweating, vaginal dryness, and mood changes like depression or anxiety. While these symptoms are not uncommon, some women do not experience any of these.
fluctuations. With menopause the cessation of menses is also marked by a decline in hormone levels and sometimes mood too. Instead of emotional ups and downs there is often more of an emotional downturn. Not all women that go through menopause have this though. The menopausal period is often characterized by many unwanted symptoms such as hot flashes, sweating, vaginal dryness, and mood changes like depression or anxiety. While these symptoms are not uncommon, some women do not experience any of these. 
 very common with acupuncture, in this article we reviewed research to find the most common so you know what to expect.
very common with acupuncture, in this article we reviewed research to find the most common so you know what to expect. hormones coordinate many aspects of our physiology and behavior such as:
hormones coordinate many aspects of our physiology and behavior such as: not the bacteria themselves but all the things that the bacteria do to the intestines and the body. Typically the bacteria that cause SIBO are the good bacteria from the colon like E. coli and other good commensal microbes. The problem is that there are too many of them.
not the bacteria themselves but all the things that the bacteria do to the intestines and the body. Typically the bacteria that cause SIBO are the good bacteria from the colon like E. coli and other good commensal microbes. The problem is that there are too many of them. between the quality of our food and the quality of our intestinal health. While it seems like a simple system, your intestinal tract if very sophisticated and termed by some as the second brain. That 30-foot pipe which makes up your intestinal system is accountable for delivering the ingredients of what you eat into your body. It is also needed for proper immune function and acts as a surveillance system to prevent entry of unwanted harmful molecules and microbes.
between the quality of our food and the quality of our intestinal health. While it seems like a simple system, your intestinal tract if very sophisticated and termed by some as the second brain. That 30-foot pipe which makes up your intestinal system is accountable for delivering the ingredients of what you eat into your body. It is also needed for proper immune function and acts as a surveillance system to prevent entry of unwanted harmful molecules and microbes.  physician, n
physician, n
 have an inherited
have an inherited  mаgnеѕium, саlсium, аnd аll оf thе B vitаminѕ diluted in water. Taking vitamins intrаvеnоuѕlу delivers еѕѕеntiаl vitаminѕ аnd nutriеntѕ dirесtlу intо thе blооd ѕtrеаm, bураѕѕing thе digеѕtivе ѕуѕtеm аnd еnаbling quiсk аbѕоrрtiоn. Often when a реrѕоn'ѕ bоdу iѕ ѕiсk оr bесоming ѕiсk thе gut iѕ аlrеаdу inflаmеd аnd mаkеѕ оrаl аbѕоrрtiоn diffiсult аnd lеѕѕ еffiсiеnt. The Myer's cocktail benefits the body by allowing еffiсiеnt аnd quick аbѕоrрtiоn whilе bооѕting еnеrgу аnd hуdrаting thе bоdу.
mаgnеѕium, саlсium, аnd аll оf thе B vitаminѕ diluted in water. Taking vitamins intrаvеnоuѕlу delivers еѕѕеntiаl vitаminѕ аnd nutriеntѕ dirесtlу intо thе blооd ѕtrеаm, bураѕѕing thе digеѕtivе ѕуѕtеm аnd еnаbling quiсk аbѕоrрtiоn. Often when a реrѕоn'ѕ bоdу iѕ ѕiсk оr bесоming ѕiсk thе gut iѕ аlrеаdу inflаmеd аnd mаkеѕ оrаl аbѕоrрtiоn diffiсult аnd lеѕѕ еffiсiеnt. The Myer's cocktail benefits the body by allowing еffiсiеnt аnd quick аbѕоrрtiоn whilе bооѕting еnеrgу аnd hуdrаting thе bоdу.

 will be discussed in the next section.
will be discussed in the next section.
 these base pairs. At specific areas within these billion of base pairs are the genes. The location and sequence of each gene is unique giving rise to genes of various lengths, sequence, and combinations of the base pairs. Regardless of this uniqueness these genes carry the information to make proteins.
these base pairs. At specific areas within these billion of base pairs are the genes. The location and sequence of each gene is unique giving rise to genes of various lengths, sequence, and combinations of the base pairs. Regardless of this uniqueness these genes carry the information to make proteins.  When it comes to training and education, there are some similarities and some differences between nutritionist and naturopathic doctors. First lets define what we mean by nutritionist. There are two titles that are thrown around somewhat interchangeably for someone that helps with diet advice. Dietitian or Registered Dietitian (RD) and Nutritionist or certified nutritionist have similar roles but different backgrounds. RD is sometimes referred to as
When it comes to training and education, there are some similarities and some differences between nutritionist and naturopathic doctors. First lets define what we mean by nutritionist. There are two titles that are thrown around somewhat interchangeably for someone that helps with diet advice. Dietitian or Registered Dietitian (RD) and Nutritionist or certified nutritionist have similar roles but different backgrounds. RD is sometimes referred to as  If your approach to
If your approach to 
 enzyme is one of thousands of enzymes in your body. So trying to correct for a deficiency here can cause more problems when there are also issues with other enzymes down stream.
enzyme is one of thousands of enzymes in your body. So trying to correct for a deficiency here can cause more problems when there are also issues with other enzymes down stream. In this article we will touch on the effects hormones can have on the body and the role of bioidentical hormone replacement therapy in treating hormonal imbalance symptoms.
In this article we will touch on the effects hormones can have on the body and the role of bioidentical hormone replacement therapy in treating hormonal imbalance symptoms. 
 Uterine Fibroids, a non-cancerous growth that can develop in or around the uterus (womb) can be a problem for around one in three women. The growths are made up of a mixture of muscle and fibrous tissue. While some women do not have any symptoms (in fact, for many, being unable to conceive is the first indication that they have fibroids), others can suffer quite significantly with heavy and painful menses. The number, size, and location of fibroids will be the main influences of your symptoms.
Uterine Fibroids, a non-cancerous growth that can develop in or around the uterus (womb) can be a problem for around one in three women. The growths are made up of a mixture of muscle and fibrous tissue. While some women do not have any symptoms (in fact, for many, being unable to conceive is the first indication that they have fibroids), others can suffer quite significantly with heavy and painful menses. The number, size, and location of fibroids will be the main influences of your symptoms. There are relatively few obese people who can tackle the weight loss journey on their own. Gradually increasing the amount of exercise, while watching what is eaten though a calorie controlled diet can result in weight loss without. Most people can start this without the help of professionals, but those who have tried know that this requires determination. In particular the ability to apply daily focus and work through any plateaus they might encounter.
There are relatively few obese people who can tackle the weight loss journey on their own. Gradually increasing the amount of exercise, while watching what is eaten though a calorie controlled diet can result in weight loss without. Most people can start this without the help of professionals, but those who have tried know that this requires determination. In particular the ability to apply daily focus and work through any plateaus they might encounter.